What is Breast Perfusion?
Breast perfusion is an imaging study of the breasts.
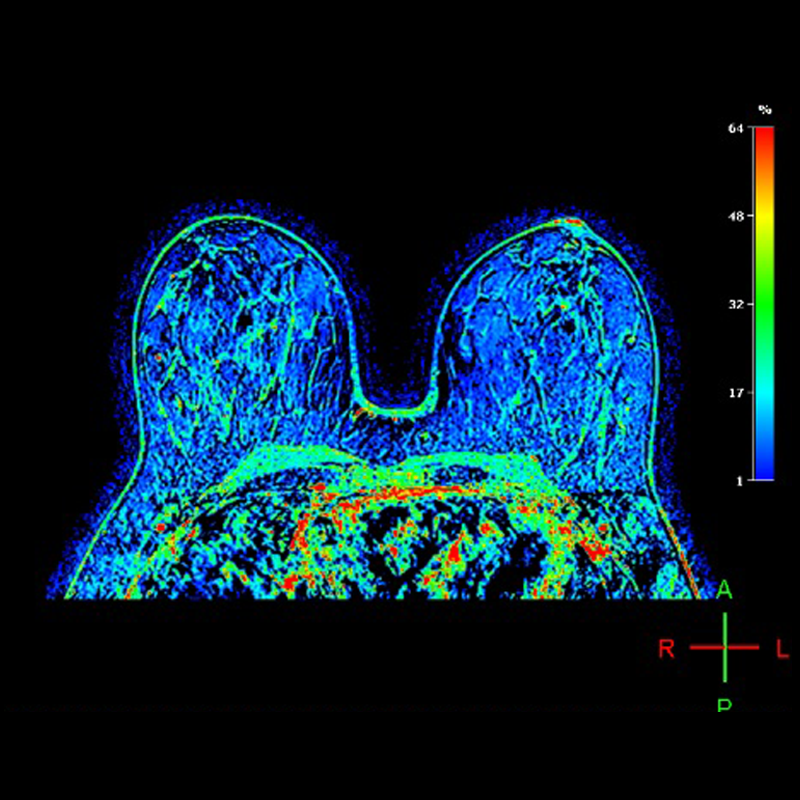
The immature blood vessels of malignant tumors differ from normal vessels by having higher permeability. Cancerous tumors require an unusually high volume blood supply to grow rapidly.
This procedure detects this unusually high volume blood supply typical with cancerous tumors. Contrast agents, will slowly fill up the larger empty spaces in normal tissues relative to the fast fill up of the lower extracellular volume fraction for cancerous tissue. The objective of this study is to identify cancerous tissue by the fill up behavior in the breasts.
"Breast perfusion gives the opportunity to observe the vascularity of the lesion, increases the sensitivity and diagnostic specificity in the early detection of breast cancer, providing information on the intensity of the signal in the region of interest, whose patterns differ if it is benign or malignant."
How to prepare for Breast Perfusion MRI at Scantibodies Imaging and Therapy?
Fast for 8 hours
Creatinine test
Have recent creatinine test results (done within the last 15 days).
Not be allergic to the contrast substance
Not be allergic to the contrast substance (gadolinium).
Doctor’s prescription
Have a doctor’s prescription for the study.
Previous scans
Bring all previous scans such as ultrasound, mastography and MRIs.
What equipment is used for Breast Perfusion MRI at Scantibodies Imaging and Therapy?
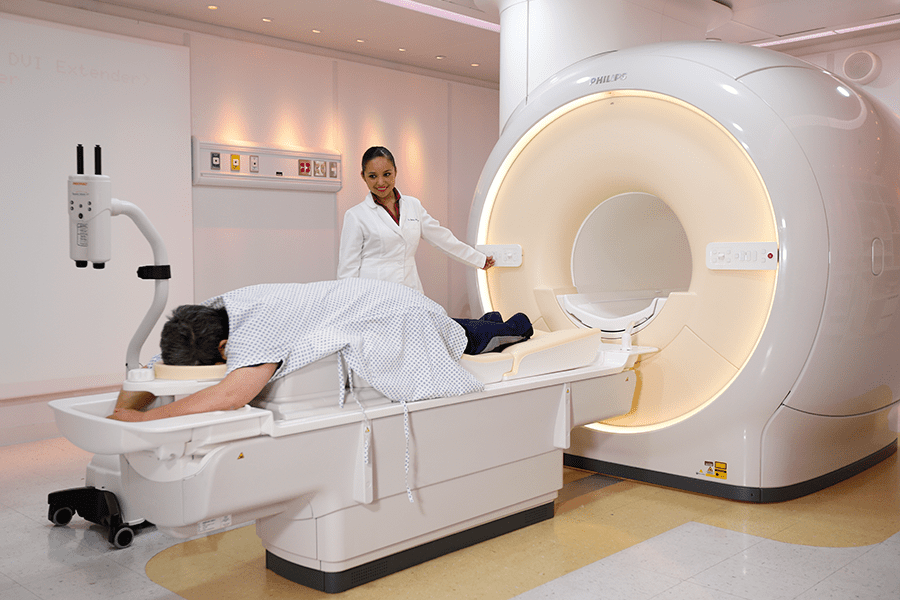
Our equipment:
The study is performed with a Digital Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) equipment, which runs with fiber optics.
At Scantibodies we use the Philips 1.5T Ingenia, one of the highest resolution MRI 1.5T system available.
Additionally, we use a Breast Antenna, in order to obtain fast images of the highest quality when performing Breast Perfusion.
Amenities:
More information about our Digital MRI services:
Breast cancer risk factors.
Every woman wants to know what she can do to lower her risk of breast cancer. Some of the factors associated with breast cancer — being a woman, your age, and your genetics, for example — can’t be changed. Other factors — being overweight, lack of exercise, smoking cigarettes, and eating unhealthy food — can be changed by making choices. By choosing the healthiest lifestyle options possible, you can empower yourself and make sure your breast cancer risk is as low as possible.
The known risk factors for breast cancer are listed below.
• Being a Woman
• 55 or older. Diagnosis of a close female relative.
• Genetics (About 5% to 10% are hereditary)
• Personal history of breast cancer
• Radiation to chest or face before age 30
• Certain breast changes Race/Ethnicity (White women) Being Overweight
• Pregnancy history (30 years or more without full term pregnancy)
• No breastfeeds for at least 1 year. Started menstruating younger than age 12. Using
• HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy)
• Drinking alcohol dense breasts
• Lack of exercise
• Smoking *
* For more information visit: breastcancer.org
How is it done?

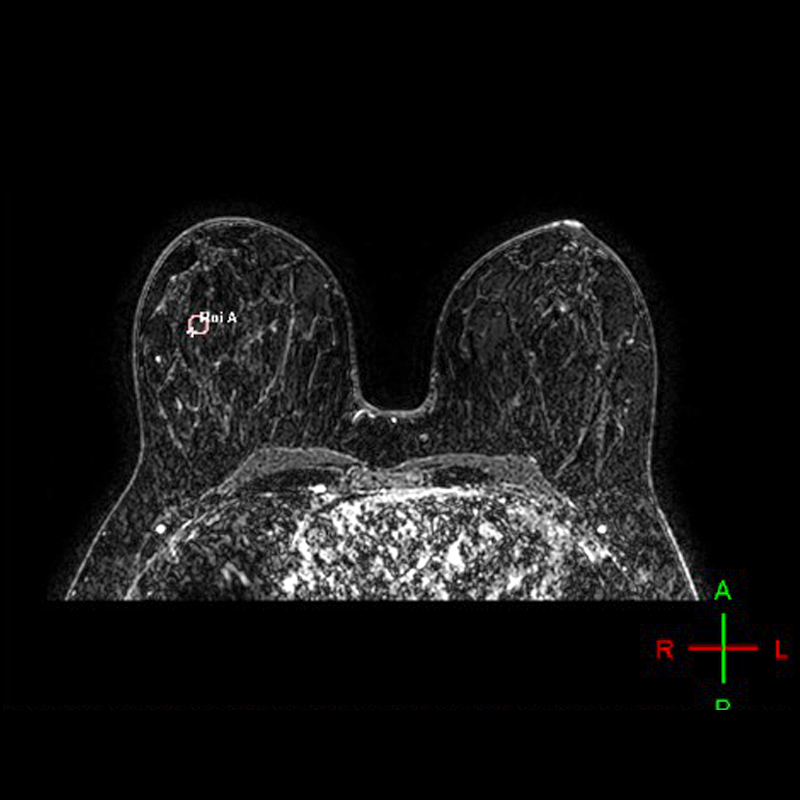
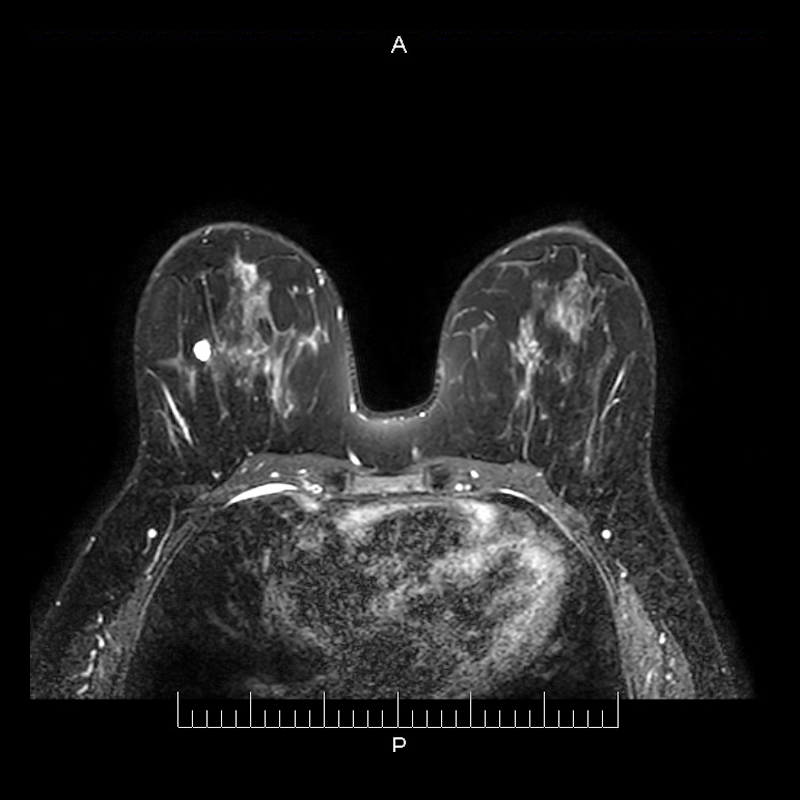
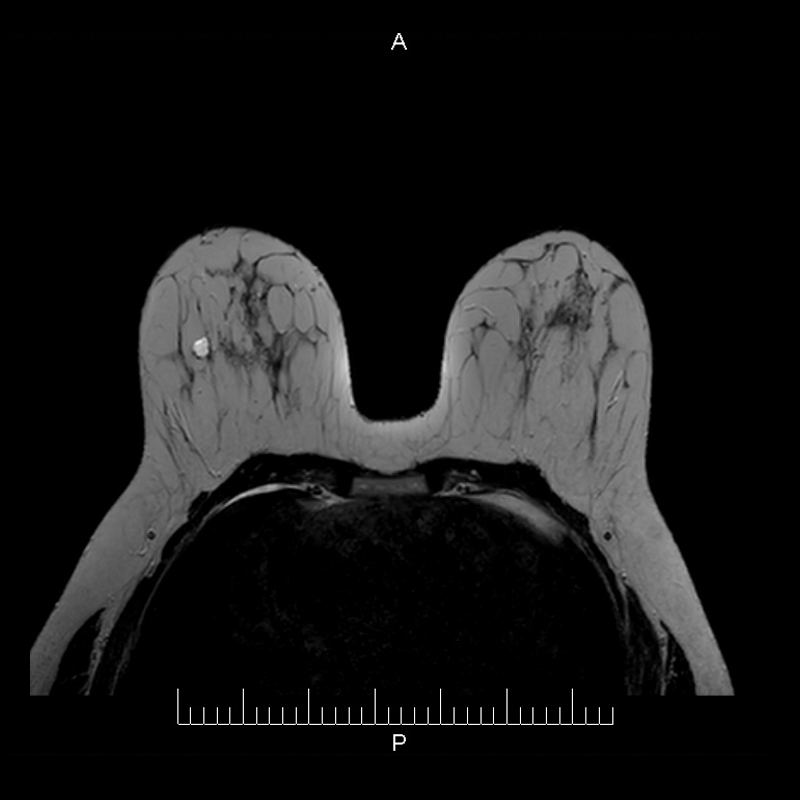
The patient lays face down on the MRI table; both breasts are positioned over a special antenna which acquires the images.

Images are first taken without the contrast substance.

An IV injection of a contrast substance (gadolinium) is applied to the patient.

Secondly perfusion images are taken with the contrast substance.

Both images are compared.
When is Breast Perfusion a useful study?
Based on medical literature, the following are some applications for this scan:
• Patients with a type of breast cancer called lobular carcinoma.
• Patients with a mutation in their genes indicating a predisposition to breast cancer.
• Patients with a tumor or mass in the armpit to investigate whether the mass originated in the breast.
• Evaluating breast implants. MRI is the best test for determining whether silicone implants have ruptured. **
Prevention is your best option.
Breast cancer signs and symptoms
The most common symptom of breast cancer is a new lump or mass. A painless, hard mass that has irregular edges is more likely to be cancer, but breast cancers can be tender, soft, or round.
They can even be painful. For this reason, it’s important to have any new breast mass, lump, or breast change checked by an experienced health care professional. Other possible symptoms of breast cancer include:
• Swelling of all or part of a breast (even if no lump is felt)
• Skin dimpling (sometimes looking like an orange peel)
• Breast or nipple pain
• Nipple retraction (turning inward)
• Nipple or breast skin that is red, dry, flaking or thickened
• Nipple discharge (other than breast milk)
• Swollen lymph nodes (Sometimes a breast cancer can spread to lymph nodes under the arm or around the collar bone and cause a lump or swelling there, even before the original tumor in the breast is large enough to be felt.) ***
“Although any of these symptoms can be caused by things other than breast cancer, if you have them, they should be reported to a health care professional so the cause can be found.”